Human Growth Hormone
Human Growth Hormone
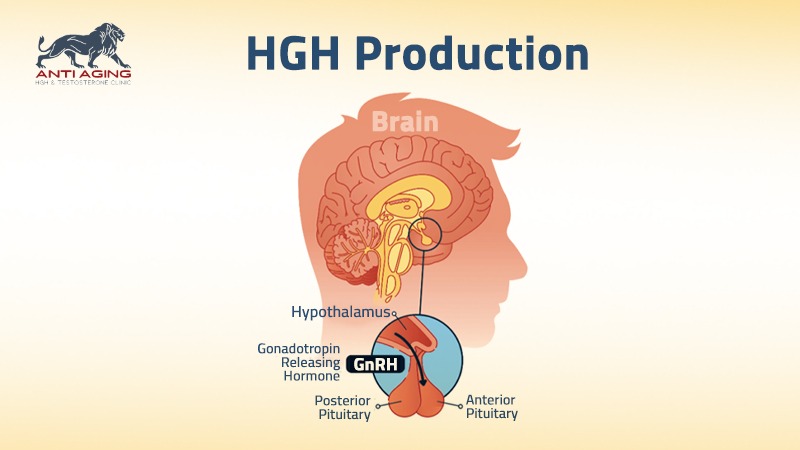
HGH is an amino acid, single chain polypeptide that the body synthesizes, stores, and secretes by using somatotropic cells in the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland.
Human Growth Hormone is a peptide hormone that stimulates human growth, cell production, and regeneration of tissue in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is a specific mitogen which only affects certain types of cells.
Bio-synthetic human growth hormone is also known as recombinant human growth hormone, it’s also commonly referred to as Somatropin, or rhGH.
The most widely known effect of growth hormone is height growth, but it serves multiple metabolic functions as well. Growth hormone increases calcium retention and strengthens bone mineralization. Muscle mass can also be increased by new muscle cell creation. Which is quite different than hypertrophy.
The effects growth hormone has on tissues of the body are generally described as anabolic, or the process of building up. As is the case with many other protein hormones, HGH acts by interacting with specific cell surface receptors. And it also promotes lipolysis, which reduces adipose tissue, most commonly known as body fat. With the exception of the brain, HGH increases protein synthesis and stimulates growth in internal organs.
The results of HGH deficiency vary significantly depending on age of occurrence. It causes failure of growth in children, resulting in shortened height. Leading to genetic conditions and congenital malformations. Sometimes leading to delayed sexual maturity. For adults, the symptoms are usually much more subtle, including physical weakness, lack of energy, reduced bone mass, and higher risk of cardiovascular problems. Sometimes causing structural lesions or trauma. However, the most noticeable effects of HGH deficiency are decreased muscle mass, weight gain, and decreased energy.
The Benefits of HGH in the body:
● Builds muscle
● Enhances immune function
● Strengthens the heart
● Helps control stress-induced damage
● Aids kidney function
● Enhances orgasmic intensity
● Lowers blood pressure
● Lowers cholesterol
● Long-term use reduces insulin requirements in diabetics
● Stimulates nerve cell growth and repair in brain, spinal cord, & peripheral nerves
● Stimulates joint repair from damaged cartilage, tendons
● Decreases body fat (particularly abdominal organs)
● Increases extracellular fluid
● Speeds healing from burns, surgery, fractures
● Restores bone loss of osteoporosis
● Reverses congestive heart failure
● Restores youthful drive & energy
● Restores pulmonary function in chronic lung disease
● Improves mood & sleep patterns
● Thickens skin, restores tone & elasticity
● Reduces susceptibility to illness
● Protects against early cancer cell formation
● Stimulates growth & repair of all organs of the body
The identification, purification, and eventual synthesis of HGH is largely credited to Choh Hao Li. The company Genentech pioneered the initial use of recombinant hgh for humans in 1981.
In 1985, bio-synthetic hgh replaced pituitary derived human growth hormone for therapeutic use in the United States and elsewhere.
A sustained release from of hgh was approved by the FDA in 1999, allowing for fewer injections.







